Understanding MRI Anatomy: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is one of the most powerful diagnostic tools used in modern medicine. It plays a critical role in imaging the body’s internal structures without the need for invasive procedures. But what exactly is MRI anatomy, and how does it work? In this guide, we will take a deep dive into MRI anatomy, focusing particularly on MRI brain anatomy, to help beginners understand the fascinating science behind MRI scans.
What is MRI Anatomy?
MRI anatomy refers to the detailed imaging and structural visualization of the human body’s tissues using Magnetic Resonance Imaging technology. Unlike X-rays or CT scans that use radiation, MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create highly detailed images of the organs, soft tissues, and bones.
The primary function of MRI is to provide an in-depth look at the internal anatomy of the body. The images produced can reveal information about the size, structure, and condition of organs and tissues, making it an indispensable tool in medical diagnostics.
The Technology Behind MRI Anatomy
MRI scans are based on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). In simple terms, MRI anatomy imaging is achieved by exploiting the magnetic properties of atoms, particularly hydrogen atoms found abundantly in the human body.
- Magnetic Field: When a patient enters the MRI machine, they are surrounded by a strong magnetic field. This field aligns the hydrogen atoms in the body.
- Radiofrequency Pulse: Once the hydrogen atoms align, a radiofrequency pulse is emitted, which causes the hydrogen atoms to flip out of alignment.
- Relaxation: As the hydrogen atoms return to their original alignment, they release energy in the form of signals.
- Signal Detection: These signals are detected by the MRI machine and processed by a computer to create detailed images.
The MRI machine can distinguish between different tissues based on their unique response to the magnetic field and radiofrequency pulse. This is how it can produce images of muscles, organs, and even the brain with remarkable clarity.
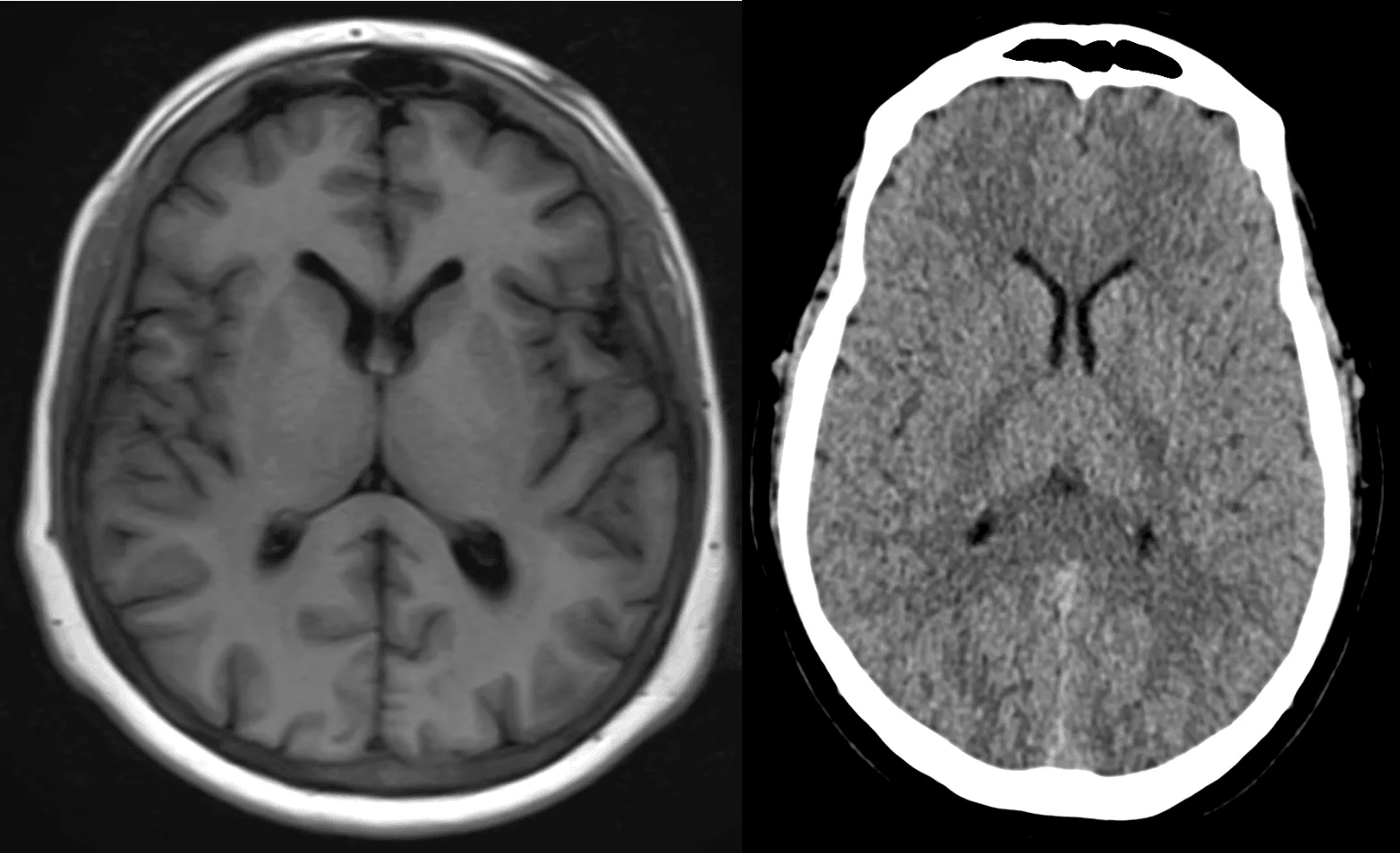
MRI Brain Anatomy: How MRI Imaging Revolutionizes Brain Diagnostics
When it comes to brain health, MRI scans are invaluable. MRI brain anatomy allows doctors and healthcare professionals to examine the brain’s structure in great detail. This is especially important for diagnosing neurological conditions such as brain tumors, strokes, aneurysms, multiple sclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Why is MRI Brain Anatomy So Important?
MRI brain anatomy is a non-invasive method for understanding the intricate structure of the brain. Here are some key benefits:
- High Resolution: MRI provides highly detailed images of the brain’s soft tissues, which is crucial for detecting abnormalities that might not show up on other imaging methods like X-rays or CT scans.
- No Radiation: Unlike other imaging technologies, MRI does not expose the patient to harmful radiation, making it a safer option for repeated imaging.
- Brain Tumors and Lesions: MRI scans are instrumental in identifying tumors, cysts, and other abnormal growths in the brain. They provide clearer images compared to CT scans, which can be crucial for early detection and treatment planning.
- Monitoring Neurological Diseases: Diseases like multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s can cause changes to the brain structure. MRI brain anatomy is often used to monitor disease progression and assess the effectiveness of treatments.
The Structure of the Brain in MRI
The MRI of the brain provides images of various structures within the brain. These include:
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher brain functions such as thought, memory, sensory processing, and voluntary muscle movements. MRI brain anatomy allows doctors to observe any abnormalities in the cerebrum that might indicate neurological issues.
- Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is responsible for coordination and motor control. MRI can detect signs of injury or diseases affecting the cerebellum.
- Brainstem: The brainstem controls vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and sleep patterns. Abnormalities in the brainstem can be seen through MRI brain imaging, which helps in diagnosing various disorders.
- Venticular System: MRI scans can also visualize the brain’s ventricles, which are fluid-filled spaces. This is important in identifying conditions like hydrocephalus, where there is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- White Matter and Gray Matter: MRI brain anatomy provides an excellent distinction between white matter (which consists of nerve fibers) and gray matter (where the brain’s processing takes place). Abnormalities in these regions can indicate conditions like multiple sclerosis or dementia.
How Does MRI Help with Neurological Diagnosis?
MRI brain anatomy is crucial for a variety of neurological conditions. Here’s how it aids in diagnosing and understanding brain-related disorders:
1. Brain Tumors and Cancers
MRI is one of the most reliable methods for detecting brain tumors. It provides detailed images of tumor size, location, and whether it’s affecting surrounding brain tissue. This helps doctors plan surgery or other treatment options, ensuring the best possible outcome for patients.
2. Stroke Diagnosis
When a stroke occurs, it disrupts blood flow to the brain, which can cause permanent damage if not treated quickly. MRI scans can identify the location and extent of the damage, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis and better treatment planning.
3. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis is a disease that affects the central nervous system, causing inflammation and damage to the protective covering of nerve fibers. MRI is commonly used to track the progression of MS by identifying plaques and lesions in the brain and spinal cord.
4. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease affect brain function over time. MRI imaging is essential for detecting early signs of these diseases, allowing doctors to intervene before the condition worsens.
5. Epilepsy
MRI brain anatomy helps in diagnosing the cause of epilepsy by locating any brain abnormalities or lesions that may be triggering seizures. It’s an essential tool for doctors when evaluating the type of epilepsy a patient might have.
The Future of MRI Brain Anatomy and Imaging
As technology advances, MRI machines are becoming even more powerful, with higher resolution and faster scan times. Innovations in MRI brain anatomy imaging, such as functional MRI (fMRI), allow doctors to visualize brain activity in real time. This opens up new possibilities in diagnosing and treating brain disorders.
In the future, MRI scans may even become more affordable and accessible, offering better outcomes for patients in remote areas.
Conclusion
MRI anatomy, especially MRI brain anatomy, is a crucial tool for medical professionals in diagnosing and treating a variety of conditions. From brain tumors to neurological diseases, MRI provides an unmatched level of detail and clarity, making it a vital part of modern medicine. By understanding the fundamentals of MRI anatomy, both patients and healthcare providers can benefit from its incredible diagnostic capabilities.